
Are you aware of the harmful effects of cigarette smoking? Cigarette smoking is a pervasive habit that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite the extensive knowledge of its dangers, the habit persists, leading to dire health consequences not only for smokers but also for those exposed to secondhand smoke. This article explores the harmful effects of cigarette smoking, covering its impact on physical health, mental well-being, environmental concerns, and societal implications.
Table of Contents
The Harmful Effects of Cigarette Smoking for Physical Health Risks
Respiratory Issues
One of the most immediate effects of cigarette smoking is its detrimental impact on the respiratory system. The inhalation of tobacco smoke introduces thousands of harmful chemicals into the lungs, including tar, nicotine, carbon monoxide, and formaldehyde. These substances lead to chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
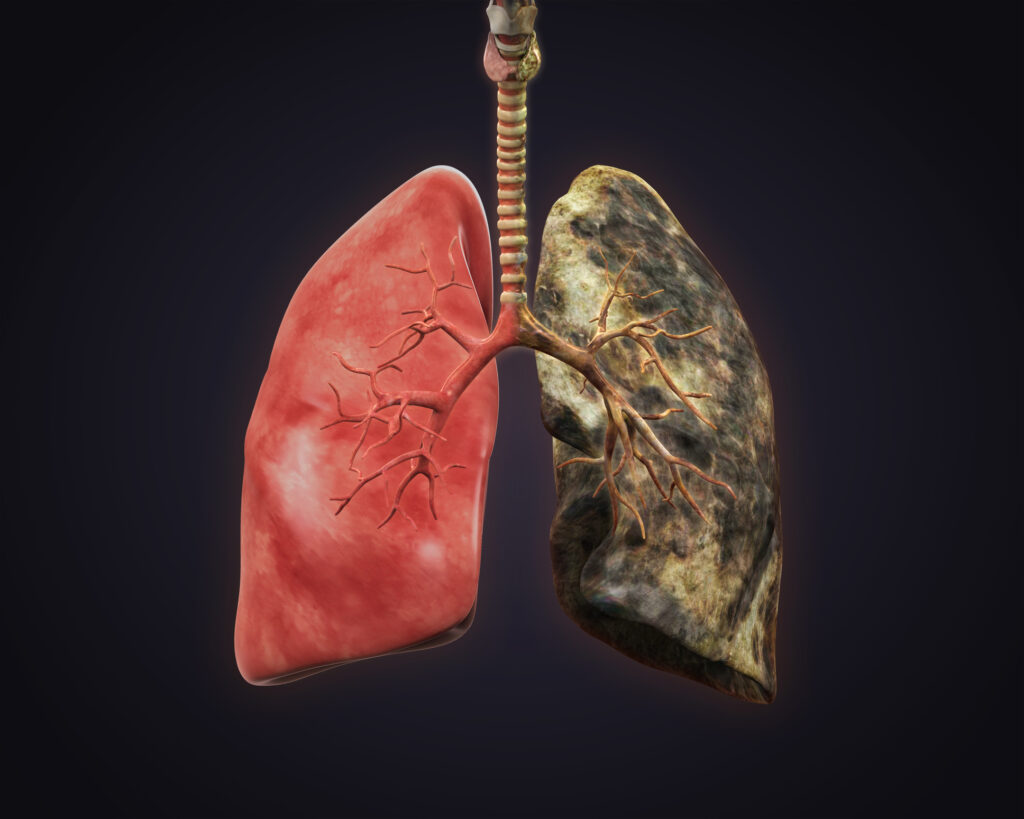
Cigarette smoke damages the lining of the airways and diminishes lung function over time. Smokers often experience chronic cough, wheezing, and shortness of breath. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), smoking is responsible for approximately 90% of lung cancer cases, making it a leading cause of cancer-related deaths.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Smoking also poses significant risks to cardiovascular health. The nicotine in cigarettes raises heart rate and blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Moreover, smoking contributes to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis—a condition that narrows and hardens the arteries, restricting blood flow.

The American Heart Association estimates that smokers are two to four times more likely to develop heart disease compared to non-smokers. Even occasional smoking can have immediate negative effects on heart health, demonstrating that no level of smoking is safe.
Cancer Risks
The link between cigarette smoking and various forms of cancer is well-established in the harmful effects of cigarette smoking. In addition to lung cancer, smoking is a major risk factor for cancers of the mouth, throat, esophagus, bladder, pancreas, stomach, and cervix—the carcinogenic compounds in cigarette smoke cause DNA damage and mutations that can lead to cancer development.
Research has shown that even light smoking increases cancer risk significantly. The more a person smokes and the longer they smoke, the higher their risk of developing these life-threatening diseases.
Impact on Immune Function

Cigarette smoking compromises the immune system, making smokers more susceptible to infections and diseases. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke interfere with the immune response, reducing the body’s ability to fight pathogens. Smokers are at a greater risk for respiratory infections like pneumonia and influenza, as well as other illnesses.
Effects on Reproductive Health

Smoking has detrimental effects on reproductive health for both men and women. In women, it can lead to complications during pregnancy, including premature birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth. Smoking during pregnancy is also associated with an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
For men, smoking can lead to erectile dysfunction and reduced fertility. The toxins in cigarettes can affect sperm quality, leading to challenges in conceiving.
Mental Health Consequences

While many people associate smoking primarily with physical health risks, it also has significant implications for mental health. Although some may use smoking as a coping mechanism for stress or anxiety, research indicates that the habit can contribute to mental health issues over time. so this is one of the harmful effects of cigarette smoking
Anxiety and Depression
Smokers are more likely to experience anxiety and depression than non-smokers. The cycle of addiction can create feelings of withdrawal and anxiety when not smoking, leading to temporary relief when lighting up. However, this relief is short-lived and often leads to increased stress and anxiety in the long run.
Furthermore, nicotine addiction can alter brain chemistry, making it difficult for individuals to manage stress and emotions effectively. This dependency can create a vicious cycle where individuals smoke more to cope with the very mental health issues that smoking exacerbates.
Cognitive Decline
Studies have shown that smoking can contribute to cognitive decline and an increased risk of dementia. The toxic substances in tobacco smoke can lead to inflammation and vascular damage in the brain, impairing cognitive function over time.
Research indicates that smokers may experience faster cognitive decline compared to non-smokers, highlighting the far-reaching consequences of tobacco use on mental acuity.
Environmental Impact

Cigarette smoking does not only harm the individual; it also has severe consequences for the environment. The production, distribution, and disposal of cigarettes contribute to environmental degradation.
Pollution and Waste

Cigarette butts are the most commonly discarded piece of waste globally. Made of plastic fibers, they can take years to decompose, posing a significant threat to ecosystems. Millions of butts end up in oceans and waterways, harming marine life and polluting the environment.
The production of tobacco also requires extensive agricultural resources. It contributes to deforestation, soil degradation, and pesticide use, leading to loss of biodiversity and ecological imbalance.
Secondhand Smoke
Secondhand smoke is a significant public health concern. Non-smokers exposed to secondhand smoke are at risk of many of the same health issues as smokers, including respiratory infections, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. According to the WHO, approximately 1.2 million people die each year due to illnesses caused by secondhand smoke exposure.
Climate Change

The tobacco industry also contributes to climate change. The cultivation and production of tobacco result in substantial greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, deforestation for tobacco farming contributes to the loss of carbon sinks, further exacerbating climate change.
Societal Implications
Cigarette smoking extends its harmful effects into the broader society, impacting public health systems and economic stability.
Economic Burden
The healthcare costs associated with smoking-related diseases are staggering. Governments and healthcare systems spend billions annually treating diseases caused by smoking. This financial burden is not only shouldered by individuals but also by taxpayers and society at large.
Lost Productivity
Smokers often experience more health-related absences from work, leading to decreased productivity. The combination of healthcare costs and lost productivity places a significant strain on the economy.
Stigmatization

As awareness of the dangers of smoking has grown, smokers often face social stigma. This can lead to feelings of isolation and shame, compounding the mental health challenges associated with nicotine addiction.
Conclusion
The harmful effects of cigarette smoking are far-reaching and multifaceted, affecting physical health, mental well-being, the environment, and society as a whole. While smoking rates have declined in many parts of the world, the battle against tobacco addiction continues.
Education and awareness about the dangers of smoking are crucial in reducing its prevalence. Public health initiatives, supportive resources for quitting, and policies aimed at reducing tobacco use are essential to protect future generations from the harmful effects of cigarette smoking. By understanding the comprehensive impact of this habit, we can work collectively to create a healthier, smoke-free world.

