
In this article, we will explore the 10 best sources of vitamin A, highlighting their benefits and nutritional profiles. Vitamin A is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining healthy vision, skin, immune function, and overall growth and development. It exists in two primary forms: preformed vitamin A (retinol) found in animal products and provitamin A carotenoids found in plant-based foods.
Table of Contents
Importance of Vitamin A
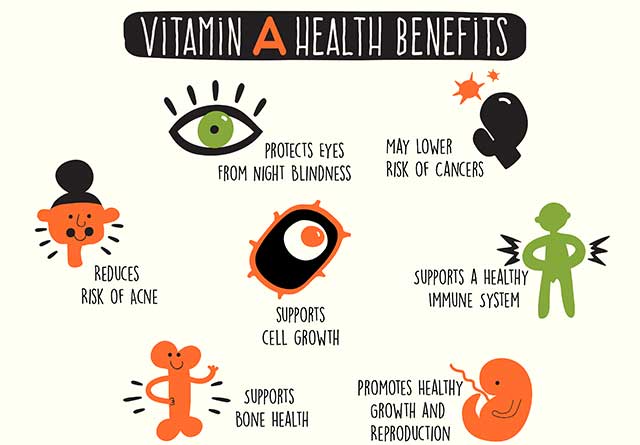
Vitamin A is essential for several bodily functions, including:
- Vision: It is a key component of rhodopsin, a protein in the eyes that helps with low-light vision.
- Immune Function: Vitamin A supports the immune system, helping the body fend off infections.
- Skin Health: It aids in the maintenance and repair of skin and mucous membranes.
- Reproductive Health: It is vital for proper reproductive function in both men and women.
- Cell Growth: Vitamin A plays a crucial role in cellular differentiation and growth.
10 Best Sources of Vitamin A
Given its importance, ensuring adequate intake of vitamin A through diet is essential. Below are ten excellent sources of this vital nutrient.
1. Liver

Overview: Animal liver is one of the 10 best sources of vitamin A. Animal liver, Particularly from beef or chicken, is one of the richest sources of vitamin A. A small serving can provide more than the daily recommended intake.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 9,442 mcg per 100g (beef liver).
- Other Nutrients: Rich in iron, B vitamins (especially B12), and folate.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 9,442 mcg |
| Iron | 6.2 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 70.7 mcg |
2. Carrots

Overview: Carrots are well known for their high beta-carotene content, a provitamin A carotenoid that the body converts into retinol.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 835 mcg per 100g (raw).
- Other Nutrients: Good source of fiber, vitamin K1, and potassium.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 835 mcg |
| Fiber | 2.8 g |
| Potassium | 237 mg |
3. Sweet Potatoes

Overview: Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of beta-carotene and provide a sweet, nutritious addition to various dishes.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 1,100 mcg per 100g (baked).
- Other Nutrients: High in fiber, vitamin C, and manganese.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 1,100 mcg |
| Fiber | 3.0 g |
| Vitamin C | 2.4 mg |
4. Spinach

Overview: Spinach is a leafy green vegetable rich in beta-carotene, making it a fantastic source of vitamin A.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 469 mcg per 100g (cooked).
- Other Nutrients: High in iron, magnesium, and vitamins C and K.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 469 mcg |
| Iron | 3.6 mg |
| Vitamin K | 482.9 mcg |
5. Kale

Overview: Kale is another leafy green that offers a wealth of nutrients, including a significant amount of vitamin A.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 481 mcg per 100g (cooked).
- Other Nutrients: High in antioxidants, vitamin C, and calcium.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 481 mcg |
| Calcium | 150 mg |
| Vitamin C | 41 mg |
6. Red Bell Peppers

Overview: Red bell peppers are not only colorful but also packed with nutrients, including vitamin A.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 157 mcg per 100g (raw).
- Other Nutrients: Excellent source of vitamin C and antioxidants.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 157 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 80.4 mg |
| Antioxidants | High |
7. Mango

Overview: This tropical fruit is delicious and rich in beta-carotene, providing a sweet way to boost vitamin A intake.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 54 mcg per 100g (raw).
- Other Nutrients: Good source of vitamin C and dietary fiber.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 54 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 36.4 mg |
| Fiber | 1.6 g |
8. Eggs

Overview: Eggs are a versatile food rich in essential nutrients, including vitamin A found in the yolk.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 140 mcg per 100g (whole eggs).
- Other Nutrients: Good source of protein, vitamin D, and B vitamins.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 140 mcg |
| Protein | 12.6 g |
| Vitamin D | 1.1 mcg |
9. Fortified Foods

Overview: Many foods, such as breakfast cereals and dairy products, are fortified with vitamin A, helping individuals meet their daily requirements easily.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Varies by product, typically around 140–500 mcg per serving.
- Other Nutrients: Often fortified with additional vitamins and minerals.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per Serving |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 140–500 mcg |
| Calcium | Varies |
| Iron | Varies |
10. Butter

Overview: Butter, especially from grass-fed cows, contains vitamin A in its retinol form.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Vitamin A Content: Approximately 684 mcg per 100g.
- Other Nutrients: Contains healthy fats and vitamin K2.
| Nutrient Content | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 684 mcg |
| Fat | 81 g |
| Vitamin K2 | 7.4 mcg |
Conclusion
Vitamin A is an essential nutrient that contributes to various bodily functions, including vision, immune health, and skin maintenance. Incorporating a variety of the foods listed above into your diet can help ensure adequate intake of this vital vitamin.
Remember that while it’s important to get enough vitamin A, balance is key. Too much vitamin A, especially in supplement form, can lead to toxicity. Therefore, focus on obtaining this nutrient from whole foods as part of a balanced diet.
By making informed dietary choices and including a mix of these top sources of vitamin A, you can support your health and well-being effectively

